

|
单细胞测序技术服务 靶向单细胞测序(lncRNA&mRNA) 单细胞测序 |
|
生物分子凝聚体研究 HyPro靶RNA临近标记技术 |
|
NGS测序技术服务 环状DNA测序(eccDNA测序) |
|
Ribo-seq Ribo seq(ribosome profiling) |
核糖体-新生肽链复合物(RNC) RNC联合 circRNA芯片 RNC联合 lncRNA芯片 RNC-seq |
|
蛋白表达定量 DIA定量蛋白质组学 Label free非标定量 TMT标记定量 PRM靶向定量 |
蛋白修饰定量 N-糖基化蛋白组学 乳酸化修饰蛋白质组学 O-GlcNAc修饰蛋白质组学 |
数谱生物独家提供Arraystar Downstream-of-Gene Transcript (DoG RNA) 芯片技术服务,助力分析和研究人类DoG RNA。该芯片包含超过13,000个探针,可以同时检测和定量DoG RNA、DoG宿主基因的pre-mRNA 以及作为其潜在调控靶点的下游重叠转录本,具有高度的准确性和特异性。
DoG RNA是一类由于转录未能正常终止、发生转录通读(transcription read-through)时,在蛋白编码基因转录终止位点之后继续转录的RNA。>>
• DoG RNA在细胞衰老中介导转录干扰;
• DoG RNA在病毒感染过程中调控基因组的三维结构。
DoG RNA形成的嵌合体RNA和环状RNA在癌症和疾病中的作用>>
全面涵盖 DoG RNA的潜在下游调控靶点:
• 与下游邻近基因正向重叠的lncRNA、circRNA;
• 嵌合体 RNA(DoG RNA宿主基因与下游邻近基因的顺式剪接产物);
• rt-circRNA(DoG RNA宿主基因与下游邻近基因的反式剪接产物);
• 与下游邻近基因反向重叠的mRNA 和 lncRNA。
Arraystar对特定剪接位点的特异性探针设计:
• 一张芯片可同时检测 DoG RNA 和所有类型的靶 RNA(Table 1);
• 保证检测的高度精确性;
• 避免测序方法繁琐而分散的计算和分析;
灵敏度高,尤其适用于DoG下游circRNA和嵌合体RNA等低丰度RNA和微量样本。
Table 1. DoG RNA芯片探针设计方法
|
RNA类型 |
探针设计策略 (图2) |
|
|
DoG RNA |
DoG宿主基因3’端 polyA元件下游3 kb处 |
|
|
DoG宿主基因的pre-mRNA |
外显子-内含子接头处 |
|
|
DoG RNA 下游靶标 |
mRNAs/LncRNAs |
外显子-外显子接头处 |
|
下游circRNAs |
反向剪接位点附近 |
|
|
转录通读circRNAs (rt-circRNAs) |
反向剪接位点附近 |
|
|
嵌合体RNAs |
顺式剪接位点附近 |
|

图1. Arraystar DoG芯片探针设计
• DoG 区域探针:检测位于DoG宿主基因3′末端polyA元件以外3 kb处的 DoG RNA,不与宿主基因重叠。
• DoG宿主基因探针: 在DoG宿主基因的pre-mRNA在外显子-内含子接头处或内含子内部设计探针,不与其成熟体mRNA重叠。
• DoG RNA下游转录本探针Downstream transcript probe: 对于DoG RNA下游的mRNA/ lncRNA/ circRNA/ 嵌合体RNA/ rt-circRNA,在成熟体mRNA的外显子-外显子接头处设计探针、在circRNA的反向剪接位点处设计探针。
Arraystar Human DoG RNA芯片包含超过14,000个探针,可同时检测和量化 DoG RNA及其潜在的调控靶点,包括DoG RNA宿主基因的pre-mRNA 、下游重叠的转录本等,具有高准确性和强特异性。
Table 2. Arraystar Human Downstream-of-Gene (DoG) RNA芯片
|
探针总数 |
14,707 |
|
探针结合位点 |
DoGs (downstream-of–gene transcripts): DoG宿主基因3’末端polyA元件以外3 kb处。 Pre-mRNAs from the DoG host genes: DoG宿主基因的pre-mRNA外显子-内含子接头处。 Downstream sense-overlapping LncRNAs of DoGs: lncRNA的外显子-外显子接头处。 Downstream sense-overlapping CircRNAs of DoGs: circRNA的反向剪接位点处。 ChimeraRNAs (mature cis-splicing products of read-through transcripts of DoG and downstream read-in chimeric genes): 嵌合体RNA的顺式剪接接头位点。 rt-circRNAs (circular RNAs produced by back-splicing of read-through transcripts): 转录通读rt-circRNA的反向剪接位点。 Downstream anti-sense overlapping lncRNAs or coding RNAs of DoGs: 成熟体RNA的外显子-外显子接头处。 Drosophila spike-in RNAs:结合果蝇来源control RNA的对照探针。 |
|
探针特异性 |
转录本特异性 |
|
DoG RNA数目 |
4,460 |
|
DoG宿主基因的 pre-mRNA数目 |
4,460 |
|
DoG RNA下游正向lncRNA数目 |
480 |
|
DoG RNA下游circRNA数目 |
1,546 |
|
嵌合体RNA数目 |
539 |
|
转录通读rt-circRNA数目 |
356 |
|
DoG RNA下游反向lncRNA数目 |
1,866 |
|
对照探针数目 |
1,000 |
|
来源数据库 |
DoG RNA: 公开发表的高分文献[1-13] 嵌合体RNA: FusionGDB2[22] , GENCODE human V44[15],公开发表的高分文献[15, 17, 21] 转录通读rt-circRNA: 公开发表的高分文献[18, 19] 对照探针: ENSEMBL BDGP6.46[16] |
|
芯片规格 |
8 x 15K |
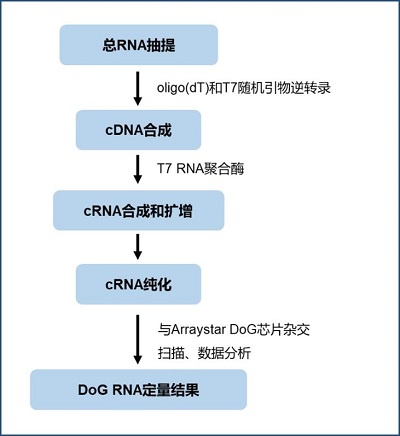
图2. Arraystar Downstream-of-Gene (DoG) RNA Microarray Profiling芯片的实验流程. 首先用oligo(dT)和T7随机引物对total RNA做逆转录合成cDNA,然后利用T7 RNA聚合酶合成cRNA,同时将Cy3荧光基团加到cRNA的3’末端,纯化后将cRNA与Arraystar DoG RNA芯片杂交并进行DoG RNA定量分析。
Arraystar DoG RNA芯片是对DoG RNA 检测和分析最灵敏、最有效和最可靠的方法,数据分析结果包括直接可使用的芯片数据、对 DoG RNA 的丰富分析和注释。
Table 3. 差异表达DoG RNA列表,包括DoG来源基因的pre-mRNA、DoG下游lncRNA等,包含系统详细的RNA注释。
|
DoG comparison (Group1 vs. Group2) |
||||
|
|
|
Differential Expression |
||
|
transcript ID |
transcript_name |
P-value <0.05 |
|log2FC|>1 |
Regulation |
|
DoCACNA1C |
DoCACNA1C |
0.0000148 |
2.28324637 |
up |
|
DoCACNA1C-pre-mRNA |
CACNA1C-pre-mRNA |
0.0000203 |
2.10372869 |
up |
|
DoCACNA1C-sense-LINC02371-202 |
LINC02371-202 |
0.0000103 |
2.52167687 |
up |
|
DoCACNA1C-antisense-ITFG2-AS1-201 |
ITFG2-AS1-201 |
0.0000671 |
-2.0136142 |
down |
|
DoACADM |
DoACADM |
0.0000115 |
-2.4050353 |
down |
|
DoACADM-pre-mRNA |
ACADM-pre-mRNA |
0.0000169 |
-2.2008475 |
down |
|
DoACADM-sense-hsa_circ_0012969 |
hsa_circ_0012969 |
0.0000107 |
-2.6164853 |
down |
|
DoACADM-rt-circRNA |
rt-circRNA-ACADM-RABGGTB-e7e2 |
0.0000059 |
-2.814912 |
down |
|
DoABR |
DoABR |
0.000000034 |
3.10297237 |
up |
|
DoABR-pre-mRNA |
ABR-pre-mRNA |
1.6E-09 |
5.44875714 |
up |
|
DoABR-sense-hsa_circ_0004931 |
hsa_circ_0004931 |
0.000000334 |
2.96418948 |
up |
|
DoABR-ChimeraRNA |
ChimeraRNA-ABR-NXN-e16e2 |
4.16E-08 |
4.49189189 |
up |
|
Annotation |
||||
|
DoGRegion |
DoGRegion |
HostGene |
Sense overlapping |
Anti-Sense overlapping |
|
chr12:2697950- |
82000 |
CACNA1C |
lncRNA ----- LINC02371-202 || LINC02371; |
lncRNA ----- ITFG2-AS1-201 || ITFG2-AS1 |
|
chr1:75763720- |
41366 |
ACADM |
CircRNA ----- hsa_circ_0012969(NM_004582 2-6/9) ; |
|
|
chr17:998017- |
5501 |
ABR |
ChimeraRNA || ABR(ENST00000302538) 1/23 || NXN(ENST00000336868) 2/8 ; |
CircRNA ----- hsa_circ_0001967(NM_013337 2-3/4) ; |
Transcript ID: DoG RNA的ID编号。
transcript_name:DoG RNA或相关转录本的名称。
P-value:评估两组DoG表达水平的差异是否具有统计学显著性的p值。
|log2FC|:差异倍数作log2转换的绝对值,表示实验组与对照组之间DoG表达水平的变化倍数。
Regulation:两组比较的上调(up)或者下调(down)。
DoGRegion_Locus:DoG RNA所在的基因组位置,以染色体号和起始、终止位置表示。
DoGRegion_Length:DoG RNA的长度,以碱基数(nt)为单位。
HostGene:DoG RNA的来源基因名称。
Sense overlapping DownstreamTranscripts:与DoG RNA在同方向上重叠的下游转录本。
Anti-Sense overlapping DownstreamTranscripts:与DoG RNA在反方向上重叠的下游转录本。

图3. DoG RNA研究路线
参考文献
1. Eaton JD et al: Xrn2 accelerates termination by RNA polymerase II, which is underpinned by CPSF73 activity. Genes Dev. 2018 Jan 15;32(2):127-139. PMID: 29432121; PMCID: PMC5830926.
2. Iwakiri J et al: Remarkable improvement in detection of readthrough downstream-of-gene transcripts by semi-extractable RNA-sequencing. RNA. 2023 Feb;29(2):170-177. PMID: 36384963; PMCID: PMC9891252.
3. Rutkowski AJ et al: Widespread disruption of host transcription termination in HSV-1 infection. Nat Commun. 2015 May 20;6:7126. PMID: 25989971; PMCID: PMC4441252.
4. Rosa-Mercado NA et al: Hyperosmotic stress alters the RNA polymerase II interactome and induces readthrough transcription despite widespread transcriptional repression. Mol Cell. 2021 Feb 4;81(3):502-513.e4. PMID: 33400923; PMCID: PMC7867636.
5. Cugusi S et al: Heat shock induces premature transcript termination and reconfigures the human transcriptome. Mol Cell. 2022 Apr 21;82(8):1573-1588.e10. PMID: 35114099; PMCID: PMC9098121.
6. Grosso AR et al: Pervasive transcription read-through promotes aberrant expression of oncogenes and RNA chimeras in renal carcinoma. Elife. 2015 Nov 17;4:e09214. PMID: 26575290; PMCID: PMC4744188.
7. Heinz S et al: Transcription Elongation Can Affect Genome 3D Structure. Cell. 2018 Sep 6;174(6):1522-1536.e22. PMID: 30146161; PMCID: PMC6130916.
8. Vilborg A et al: Widespread Inducible Transcription Downstream of Human Genes. Mol Cell. 2015 Aug 6;59(3):449-61. PMID: 26190259; PMCID: PMC4530028.
9. Hennig T et al: HSV-1-induced disruption of transcription termination resembles a cellular stress response but selectively increases chromatin accessibility downstream of genes. PLoS Pathog. 2018 Mar 26;14(3):e1006954. PMID: 29579120; PMCID: PMC5886697.
10. Dasilva LF et al: Integrator enforces the fidelity of transcriptional termination at protein-coding genes. Sci Adv. 2021 Nov 5;7(45):eabe3393. PMID: 34730992; PMCID: PMC8565846.
11. Roth SJ et al: ARTDeco: automatic readthrough transcription detection. BMC Bioinformatics. 2020 May 26;21(1):214. PMID: 32456667; PMCID: PMC7249449.
12. Wiesel Y et al: DoGFinder: a software for the discovery and quantification of readthrough transcripts from RNA-seq. BMC Genomics. 2018 Aug 8;19(1):597. PMID: 30089468; PMCID: PMC6083495.
13. Shah N et al: Tyrosine-1 of RNA Polymerase II CTD Controls Global Termination of Gene Transcription in Mammals. Mol Cell. 2018 Jan 4;69(1):48-61.e6. PMID: 29304333.
14. Glažar P et al: circBase: a database for circular RNAs. RNA. 2014 Nov;20(11):1666-70. PMID: 25234927; PMCID: PMC4201819.
15. Harrow J et al: GENCODE: the reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Res. 2012 Sep;22(9):1760-74. PMID: 22955987; PMCID: PMC3431492.
16. Birney E et al: An overview of Ensembl. Genome Res. 2004 May;14(5):925-8. PMID: 15078858; PMCID: PMC479121.
17. Grosso AR et al: Pervasive transcription read-through promotes aberrant expression of oncogenes and RNA chimeras in renal carcinoma. Elife. 2015 Nov 17;4:e09214. PMID: 26575290; PMCID: PMC4744188.
18. Vo JN et al: The Landscape of Circular RNA in Cancer. Cell. 2019 Feb 7;176(4):869-881.e13. PMID: 30735636; PMCID: PMC6601354.
19. Zhang Y et al. The Biogenesis of Nascent Circular RNAs. Cell Rep. 2016 Apr 19;15(3):611-624. PMID: 27068474.
20. Liang D et al. The Output of Protein-Coding Genes Shifts to Circular RNAs When the Pre-mRNA Processing Machinery Is Limiting. Mol Cell. 2017 Dec 7;68(5):940-954.e3. PMID: 29174924; PMCID: PMC5728686.
21. Varley KE et al. Recurrent read-through fusion transcripts in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Jul;146(2):287-97. PMID: 24929677; PMCID: PMC4085473.
22. Kim P et al. FusionGDB 2.0: fusion gene annotation update aided by deep learning. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Nov 10
23. Morgan M. et al. It's a DoG-eat-DoG world-altered transcriptional mechanisms drive downstream-of-gene (DoG) transcript production. Mol Cell. 2022; 82(11):1981-1991 [PMID:35487209]
24. Lai F. et al. Directed RNase H Cleavage of Nascent Transcripts Causes Transcription Termination. Mol Cell. 2020; 77(5):1032-1043.e4 [PMID:31924447]
25. RodrÃguez-Molina JB. et al. Knowing when to stop: Transcription termination on protein-coding genes by eukaryotic RNAPII. Mol Cell. 2023; 83(3):404-415 [PMID:36634677]
26. Hao JD et al: DDX21 mediates co-transcriptional RNA m(6)A modification to promote transcription termination and genome stability. Mol Cell 2024; 84(9):1711-1726 e1711.[PMID: 38569554]

