|
单细胞测序技术服务 靶向单细胞测序(lncRNA&mRNA) 单细胞测序 |
|
生物分子凝聚体研究 HyPro靶RNA临近标记技术 |
|
NGS测序技术服务 环状DNA测序(eccDNA测序) |
|
Ribo-seq Ribo seq(ribosome profiling) |
核糖体-新生肽链复合物(RNC) RNC联合 circRNA芯片 RNC联合 lncRNA芯片 RNC-seq |
|
蛋白表达定量 DIA定量蛋白质组学 Label free非标定量 TMT标记定量 PRM靶向定量 |
蛋白修饰定量 N-糖基化蛋白组学 乳酸化修饰蛋白质组学 O-GlcNAc修饰蛋白质组学 |
相关服务
相关产品
相关资源
芯片更适用于低丰度RNA分析small RNA通常是指长度小于200 nt的非编码小分子RNA,包括miRNA、tRF&tiRNA、sdRNA(single-stranded DNAdamage-associated sRNA)等,它们能够通过调控基因表达,在细胞生长、发育、代谢等多种生物学过程中发挥重要作用;新的研究发现,这些小分子RNA也可以与蛋白质一起直接结合染色质DNA,参与和调控DNA损伤修复、直接或间接地影响染色质的结构和修饰,最终调节基因转录情况,这些小RNA被称为染色质相关small RNA,它们与癌症等疾病的发生发展密切相关,具有临床治疗潜力[1]。
染色质相关small RNA功能一:miRNA与染色质结合抑制基因转录
在人乳腺癌细胞的衰老进程中,细胞质中的miRNA MiR-let7f可与Ago2蛋白结合,并一同转运和滞留到细胞核中,与蛋白Rb1/E2F结合之后招募组蛋白去乙酰化酶(HDACs)和组蛋白甲基化酶(HMTs),导致E2F目的基因启动子区的抑制性修饰H3K9me2、H3K27me3增加,最终使这些目的基因的表达量降低。
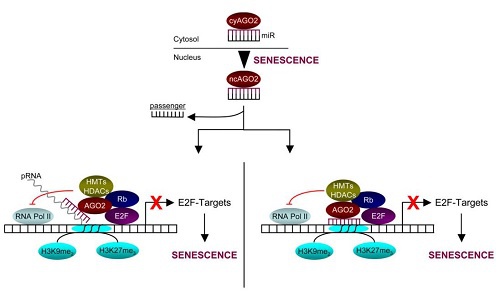
图1. miRNA-AGO复合物在核内滞留并与染色质结合,介导转录抑制[2]。
染色质相关small RNA功能二:sdRNA调控基因组DNA损伤修复
单链DNA损伤相关小RNA(single-stranded DNA damage-associated sRNA, sdRNA)是在基因组DNA产生单链断裂的情况下,由BRCA1蛋白复合物加工切割产生的小RNA。sdRNA能够招募PalB2/Rad52蛋白,修复DNA断裂位点,这种修复在肿瘤组织、正常组织和干细胞中都有出现,在临床上有重要的治疗前景[3]。
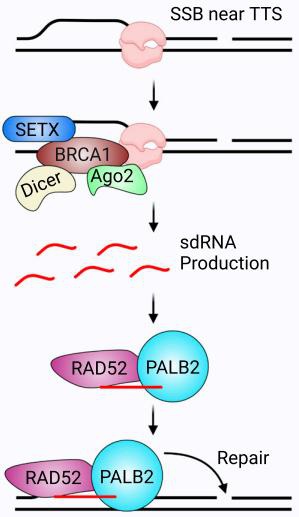
图2. sdRNA在DNA单链断裂位点附近产生并促进损伤修复,有助于抑制肿瘤发生[4]。
参考文献:
1. Arroyo, J.D., et al., Argonaute2 complexes carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011. 108(12): p. 5003-8.
2. Benhamed, M., et al., Senescence is an endogenous trigger for microRNA-directed transcriptional gene silencing in human cells. Nat Cell Biol, 2012. 14(3): p. 266-75.
3. Hatchi, E., et al., BRCA1 and RNAi factors promote repair mediated by small RNAs and PALB2-RAD52. Nature, 2021. 591(7851): p. 665-670.
4. Durut, N. and O. Mittelsten Scheid, The Role of Noncoding RNAs in Double-Strand Break Repair. Front Plant Sci, 2019. 10: p. 1155.
Aksomics(原康成生物)是Arraystar中国区唯一代理商,独家为您提供Arraystar染色质相关small RNA芯片全程一站式技术服务。您只需要提供保存完好的组织或细胞标本,Aksomics的芯片技术服务人员就可为您完成全部实验操作,并提供完整的实验报告。同时,根据您的研究需要,Aksomics还提供各种深入数据挖掘服务。
染色质相关Small RNA 检测使用的Arraystar Small RNA芯片列表
|
服务名称 |
描述 |
规格 |
|
Arraystar Human Small RNA芯片 |
miRNAs, pre-miRNAs, tRFs&tiRNAs, snoRNAs, Agotron, sdRNA |
8 x 15K |
|
Arraystar mouse Small RNA芯片 |
miRNAs, pre-miRNAs, tRFs&tiRNAs, snoRNAs |
8 x 15K |
|
Arraystar rat Small RNA芯片 |
miRNAs, pre-miRNAs, tRFs&tiRNAs, snoRNAs |
8 x 15K |
染色质相关small RNA高通量筛选鉴定是利用small RNA与染色质结合的特性,对细胞核中染色质及其结合的small RNA进行分离并抽提纯化进行检测的方法,能够分离和鉴定的small RNA包括miRNA、tRF&tiRNA
、sdRNA等,进行small RNA芯片或测序筛选后,即可获得能够结合染色质蛋白进行基因表达调控和促进损伤修复的small RNA。
样本用量:细胞用量10^6-10^7个;组织>50mg。
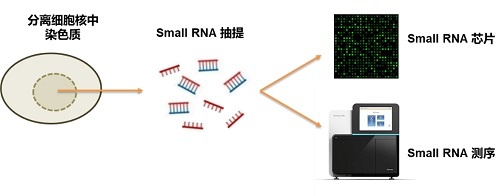
染色质相关small RNA芯片:
1.细胞/组织裂解,分离细胞核染色质;
2.small RNA抽提纯化;
3.small RNA 3’去磷酸化,DMSO变性,Cy3标记;
4.与Arraystar small RNA芯片杂交;
5.扫描芯片,进行数据分析;
6.提供结果报告。
染色质相关small RNA芯片服务利用small RNA与染色质结合的亲和性,包括miRNA、tRF&tiRNA、sdRNA等,将它们从细胞核染色质中分离出来,然后进行纯化和芯片检测,进而发现能够与染色质相互作用、调节基因表达或促进DNA修复的small RNA。
染色质相关small RNA芯片技术优势
染色质相关small RNA芯片能同时检测miRNA、tRF&tiRNA、sdRNA、snoRNA等多种small RNA,覆盖范围广;
可区分染色质与核质成分,特异性分离结合染色质small RNA进行芯片检测;
芯片探针检测特异性高,RNA直接标记,操作简单,样本需求量少。
Arraystar染色质相关small RNA芯片(human)
miRNAs
2,628
pre-miRNAs
1,745
成熟tRNAs
346
snoRNAs
956
Agotron
81
sdRNA
212
Small RNA来源数据库
miRNA: miRBase(v22)
pre-miRNA: miRBase(v22)
tRF&tiRNA: tRFdb, MINTbase, GtRNADb
snoRNA: ENSEMBL(v99)
已发表高分文献
Arraystar染色质相关small RNA芯片(mouse/rat)数据库>>
References
1. Guzzi N et al: Pseudouridylation of tRNA-Derived Fragments Steers Translational Control in Stem Cells. Cell 2018, 173(5):1204-1216 e1226.[PMID: 29628141]
2. Keam SP et al: The human Piwi protein Hiwi2 associates with tRNA-derived piRNAs in somatic cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2014, 42(14):8984-8995.[PMID: 25038252]
3. Keam SP, Sobala A, Ten Have S, Hutvagner G: tRNA-Derived RNA Fragments Associate with Human Multisynthetase Complex (MSC) and Modulate Ribosomal Protein Translation. J Proteome Res 2017, 16(2):413-420.[PMID: 27936807]
4. Zhang X et al: IL-4 Inhibits the Biogenesis of an Epigenetically Suppressive PIWI-Interacting RNA To Upregulate CD1a Molecules on Monocytes/Dendritic Cells. J Immunol 2016, 196(4):1591-1603.[PMID: 26755820]
5. Honda S et al: The biogenesis pathway of tRNA-derived piRNAs in Bombyx germ cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45(15):9108-9120.[PMID: 28645172]
6. Cole C et al: Filtering of deep sequencing data reveals the existence of abundant Dicer-dependent small RNAs derived from tRNAs. RNA 2009, 15(12):2147-2160.[PMID: 19850906]
7. Sobala A, Hutvagner G: Small RNAs derived from the 5' end of tRNA can inhibit protein translation in human cells. RNA Biol 2013, 10(4):553-563.[PMID: 23563448]
8. Lee YS, Shibata Y, Malhotra A, Dutta A: A novel class of small RNAs: tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs). Genes Dev 2009, 23(22):2639-2649.[PMID: 19933153]
9. Huang B et al: tRF/miR-1280 Suppresses Stem Cell-like Cells and Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res 2017, 77(12):3194-3206.[PMID: 28446464]
10. Kuscu C et al: tRNA fragments (tRFs) guide Ago to regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally in a Dicer-independent manner. RNA 2018, 24(8):1093-1105.[PMID: 29844106]
11. Kim HK et al: A transfer-RNA-derived small RNA regulates ribosome biogenesis. Nature 2017, 552(7683):57-62.[PMID: 29186115]
12. Kim HK et al: A tRNA-Derived Small RNA Regulates Ribosomal Protein S28 Protein Levels after Translation Initiation in Humans and Mice. Cell Rep 2019, 29(12):3816-3824 e3814.[PMID: 31851915]
13. Yeung ML et al: Pyrosequencing of small non-coding RNAs in HIV-1 infected cells: evidence for the processing of a viral-cellular double-stranded RNA hybrid. Nucleic Acids Res 2009, 37(19):6575-6586.[PMID: 19729508]
14. Schorn AJ, Gutbrod MJ, LeBlanc C, Martienssen R: LTR-Retrotransposon Control by tRNA-Derived Small RNAs. Cell 2017, 170(1):61-71 e11.[PMID: 28666125]
15. Maute RL et al: tRNA-derived microRNA modulates proliferation and the DNA damage response and is down-regulated in B cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110(4):1404-1409.[PMID: 23297232]
16. Ruggero K et al: Small noncoding RNAs in cells transformed by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1: a role for a tRNA fragment as a primer for reverse transcriptase. J Virol 2014, 88(7):3612-3622.[PMID: 24403582]
17. Falconi M et al: A novel 3'-tRNA(Glu)-derived fragment acts as a tumor-suppressor in breast cancer by targeting nucleolin. FASEB J 2019:fj201900382RR.[PMID: 31560576]
18. Zhou K et al: A tRNA fragment, tRF5-Glu, regulates BCAR3 expression and proliferation in ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8(56):95377-95391.[PMID: 29221134]
19. Goodarzi H et al: Endogenous tRNA-Derived Fragments Suppress Breast Cancer Progression via YBX1 Displacement. Cell 2015, 161(4):790-802.[PMID: 25957686]
20. Natt D et al: Human sperm displays rapid responses to diet. PLoS Biol 2019, 17(12):e3000559.[PMID: 31877125]
21. Veneziano D et al: Dysregulation of different classes of tRNA fragments in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116(48):24252-24258.[PMID: 31723042]
22. Haussecker D et al: Human tRNA-derived small RNAs in the global regulation of RNA silencing. RNA 2010, 16(4):673-695.[PMID: 20181738]
23. Balatti V et al: tRF&tiRNA signatures in cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2017, 114(30):8071-8076.[PMID: 28696308]
24. Cho H et al: Regulation of La/SSB-dependent viral gene expression by pre-tRNA 3' trailer-derived tRNA fragments. Nucleic Acids Res 2019, 47(18):9888-9901.[PMID: 31504775]
25. Babiarz JE et al: Mouse ES cells express endogenous shRNAs, siRNAs, and other Microprocessor-independent, Dicer-dependent small RNAs. Genes Dev 2008, 22(20):2773-2785.[PMID: 18923076]
26. Hasler D et al: The Lupus Autoantigen La Prevents Mis-channeling of tRNA Fragments into the Human MicroRNA Pathway. Mol Cell 2016, 63(1):110-124.[PMID: 27345152]
27. Pekarsky Y et al: Dysregulation of a family of short noncoding RNAs, tRFs&tiRNAs, in human cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2016, 113(18):5071-5076.[PMID: 27071132]
28. Liao JY et al: Deep sequencing of human nuclear and cytoplasmic small RNAs reveals an unexpectedly complex subcellular distribution of miRNAs and tRNA 3' trailers. PLoS One 2010, 5(5):e10563.[PMID: 20498841]
29. La Ferlita A et al: Identification of tRNA-derived ncRNAs in TCGA and NCI-60 panel cell lines and development of the public database tRFexplorer. Database (Oxford) 2019, 2019.[PMID: 31735953]
30. Honda S et al: Sex hormone-dependent tRNA halves enhance cell proliferation in breast and prostate cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2015, 112(29):E3816-3825.[PMID: 26124144]
31. Donovan J, Rath S, Kolet-Mandrikov D, Korennykh A: Rapid RNase L-driven arrest of protein synthesis in the dsRNA response without degradation of translation machinery. RNA 2017, 23(11):1660-1671.[PMID: 28808124]
32. Hanada T et al: CLP1 links tRNA metabolism to progressive motor-neuron loss. Nature 2013, 495(7442):474-480.[PMID: 23474986]
33. Saikia M et al: Angiogenin-cleaved tRNA halves interact with cytochrome c, protecting cells from apoptosis during osmotic stress. Mol Cell Biol 2014, 34(13):2450-2463.[PMID: 24752898]
34. Wang Q et al: Identification and functional characterization of tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs) in respiratory syncytial virus infection. Mol Ther 2013, 21(2):368-379.[PMID: 23183536]
35. Deng J et al: Respiratory Syncytial Virus Utilizes a tRNA Fragment to Suppress Antiviral Responses Through a Novel Targeting Mechanism. Mol Ther 2015, 23(10):1622-1629.[PMID: 26156244]
36. Zhou J et al: Identification of two novel functional tRNA-derived fragments induced in response to respiratory syncytial virus infection. J Gen Virol 2017, 98(7):1600-1610.[PMID: 28708049]
37. Yang X et al: 5-methylcytosine promotes mRNA export - NSUN2 as the methyltransferase and ALYREF as an m(5)C reader. Cell Res 2017, 27(5):606-625.[PMID: 28418038]
38. Ivanov P et al: Angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments inhibit translation initiation. Mol Cell 2011, 43(4):613-623.[PMID: 21855800]
39. Ivanov P et al: G-quadruplex structures contribute to the neuroprotective effects of angiogenin-induced tRNA fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2014, 111(51):18201-18206.[PMID: 25404306]
40. Schaffer AE et al: CLP1 founder mutation links tRNA splicing and maturation to cerebellar development and neurodegeneration. Cell 2014, 157(3):651-663.[PMID: 24766810]
41. Hansen, T et al: Argonaute-associated short introns are a novel class of gene regulators. Nat Commun 2016, 11538 (7). [PMID:
1. 差异表达的small RNA注释信息表格
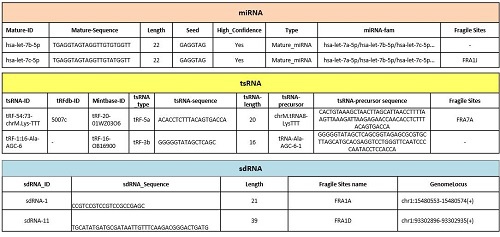
2. 深入统计分析:差异表达的染色质相关small RNA火山图、散点图、聚类图