

|
单细胞测序技术服务 靶向单细胞测序(lncRNA&mRNA) 单细胞测序 |
|
生物分子凝聚体研究 HyPro靶RNA临近标记技术 |
|
NGS测序技术服务 环状DNA测序(eccDNA测序) |
|
Ribo-seq Ribo seq(ribosome profiling) |
核糖体-新生肽链复合物(RNC) RNC联合 circRNA芯片 RNC联合 lncRNA芯片 RNC-seq |
|
蛋白表达定量 DIA定量蛋白质组学 Label free非标定量 TMT标记定量 PRM靶向定量 |
蛋白修饰定量 N-糖基化蛋白组学 乳酸化修饰蛋白质组学 O-GlcNAc修饰蛋白质组学 |
RNA G-四联体 (RNA G-quadruplexes,rG4)是由富含鸟嘌呤 (G) 的RNA序列通过Hoogsteen氢键形成的一种非经典二级结构。该结构由堆叠的G-四分体平面构成,并由K⁺等单价阳离子稳定(图1)。rG4的动态结构转变可调控RNA转录[1]、染色质修饰因子募集[2]、miRNA前体加工[3]、mRNA翻译[4, 5]以及 mRNA 稳定性[6]。此外,rG4 还能与m7G [3]、o8G[7]和m6A[8, 9]等 RNA 修饰共同调控基因表达。rG4形成发生失调,则会影响应激反应 [7]、癌症基因表达调控 [10, 11],并与帕金森病、路易体痴呆及多系统萎缩中发生的α-突触核蛋白聚集有关[12]。
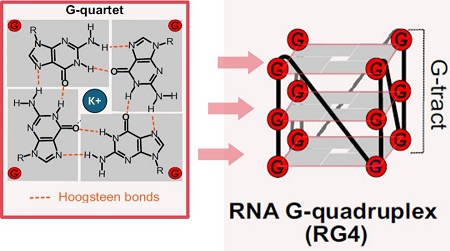
图1: 在富含鸟嘌呤的RNA序列中,四个鸟嘌呤通过Hoogsteen键结合形成G-四分体平面,G-四分体平面堆叠形成RNA G-四联体(RG4)[13]。
Arraystar (in vivo)rG4芯片技术可精准定量转录组中的rG4 结构。其中的关键步骤包括:体内硫酸二甲酯 (Dimethyl sulfate, DMS) 处理、体外RNA重折叠,以及使用抗G4抗体(BG4)进行亲和性捕获。随后,将捕获到的含有 rG4结构的 RNA进行去甲基化处理,以去除 DMS 处理所产生的副产物m1A/m3C,消除其造成的检测干扰。最后,利用高灵敏度的Arraystar (in vivo)rG4芯片探针对rG4-RNA进行定量分析。Arraystar (in vivo)rG4芯片技术不仅能够有效捕获和检测活细胞中的rG4,同时也消除了DMS诱导的修饰所产生的偏差,从而显著提高了rG4 定量图谱分析结果的准确性和可靠性。
服务名称
物种
规格
Arraystar (in vivo)rG4芯片服务
Human
8 x 15K
技术优势:
1. 体内DMS处理与体外重折叠复现了真实的rG4结构
2. 使用高亲和性的BG4抗体特异性富集含有rG4结构的RNA
3. Demethylation处理去除了DMS 处理的副产物m1A/m3C所造成的检测干扰
4. Arraystar (in vivo)rG4芯片可以灵敏的检测rG4 RNA, 包括RNA测序无法准确检测的低丰度RNA
参考文献:
1. Yari H et al: LncRNA REG1CP promotes tumorigenesis through an enhancer complex to recruit FANCJ helicase for REG3A transcription. Nat Commun 2019, 10(1):5334.[PMID: 31767869]
2. Lee YW, Weissbein U, Blum R, Lee JT: G-quadruplex folding in Xist RNA antagonizes PRC2 activity for stepwise regulation of X chromosome inactivation. Mol Cell 2024, 84(10):1870-1885 e1879.[PMID: 38759625]
3. Pandolfini L et al: METTL1 Promotes let-7 MicroRNA Processing via m7G Methylation. Mol Cell 2019, 74(6):1278-1290 e1279.[PMID: 31031083]
4. Arora A, Suess B: An RNA G-quadruplex in the 3' UTR of the proto-oncogene PIM1 represses translation. RNA Biol 2011, 8(5):802-805.[PMID: 21734463]
5. Song J, Perreault JP, Topisirovic I, Richard S: RNA G-quadruplexes and their potential regulatory roles in translation. Translation (Austin) 2016, 4(2):e1244031.[PMID: 28090421]
6. Rouleau S et al: 3' UTR G-quadruplexes regulate miRNA binding. RNA 2017, 23(8):1172-1179.[PMID: 28473452]
7. Ma Y et al: RNA G-Quadruplex within the 5'-UTR of FEN1 Regulates mRNA Stability under Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 2023, 12(2).[PMID: 36829835]
8. Yoshida A et al: Recognition of G-quadruplex RNA by a crucial RNA methyltransferase component, METTL14. Nucleic Acids Res 2022, 50(1):449-457.[PMID: 34908152]
9. Jara-Espejo M, Fleming AM, Burrows CJ: Potential G-Quadruplex Forming Sequences and N(6)-Methyladenosine Colocalize at Human Pre-mRNA Intron Splice Sites. ACS Chem Biol 2020, 15(6):1292-1300.[PMID: 32396327]
10. Anastasakis DG et al: Nuclear PKM2 binds pre-mRNA at folded G-quadruplexes and reveals their gene regulatory role. Mol Cell 2024, 84(19):3775-3789 e3776.[PMID: 39153475]
11. Kharel P, Ivanov P: PKM2-G-quadruplex interactions conspire to regulate the cancer transcriptome. Mol Cell 2024, 84(19):3574-3575.[PMID: 39366344]
12. Matsuo K et al: RNA G-quadruplexes form scaffolds that promote neuropathological alpha-synuclein aggregation. Cell 2024, 187(24):6835-6848 e6820.[PMID: 39426376]
13. Dumas L et al: G-Quadruplexes in RNA Biology: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Trends Biochem Sci 2021, 46(4):270-283.[PMID: 33303320]
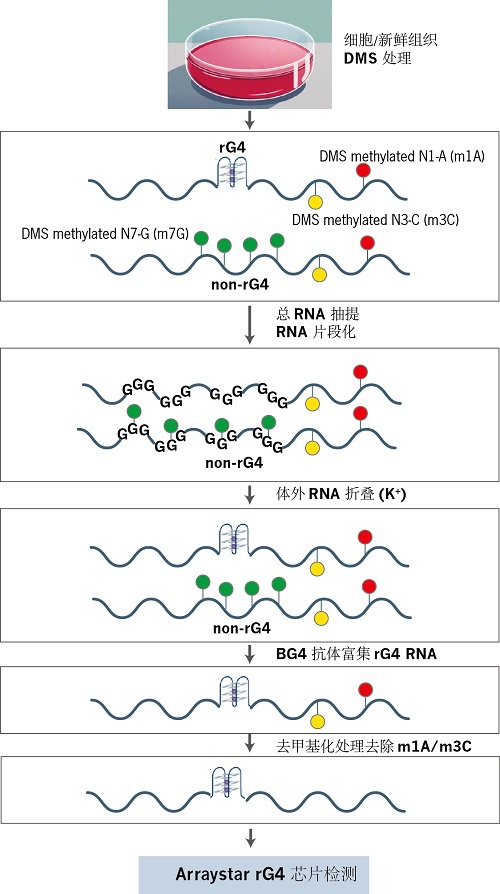
1.体内 DMS 处理
培养细胞经硫酸二甲酯(DMS)处理,对 RNA 中的腺嘌呤(A)、胞嘧啶(C)及非 rG4折叠区域的鸟嘌呤(G)进行甲基化修饰。rG4 结构内的 G 碱基因空间位阻不受影响,从而保留其未甲基化状态。
2.RNA 抽提与体外重折叠
分离总 RNA 并进行片段化处理,随后在含K⁺的缓冲体系中经历变性-复性过程。此步骤仅允许细胞内原有的 rG4 区域特异性重折叠,而其他区域由于携带m7G修饰,无法形成稳定结构。
3.rG4 免疫沉淀
利用抗 G-四联体抗体(BG4)对含 rG4 结构的 RNA 进行免疫沉淀(IP),实现目标分子的特异性富集。
4.去甲基化与反转录
富集的 RNA 经去甲基化处理,清除 DMS 诱导的副产物(如 m¹A/m³C),消除检测偏差。随后通过反转录合成双链 cDNA,并引入T7 启动子序列。
5.荧光标记 cRNA 合成
以 cDNA 为模板,T7 RNA 聚合酶催化体外转录反应,掺入Cy3-CTP 荧光染料,生成带Cy3 标记的反义 cRNA。
6.芯片杂交与数据分析
标记的 cRNA 与Arraystar (in vivo)rG4 芯片杂交,通过荧光信号定量分析转录组中rG4 结构的分布与丰度。
Arraystar (in vivo)Human rG4芯片参数
|
Arraystar (in vivo)Human rG4芯片 |
|
|
总探针数 |
14,708 |
|
rG4探针数 |
13,708 |
|
3'-UTR rG4位点 |
5,097 |
|
5'-UTR rG4位点 |
1,697 |
|
CDS rG4位点 |
3,053 |
|
lncRNA rG4位点 |
3,861 |
|
Spike-in探针 |
1,000 |
|
rG4信息来源数据库 |
rG4s: literatures[1-14], G4Atlas[15], QUADRatlas[16] G4s: EndoQuad[17], G4Bank[18] |
|
Spike-in来源 |
ENSEMBL BDGP6.46[19] |
|
芯片规格 |
8 x 15K |
RNA G-quadruplex (rG4) 数据库
数据库
简介
链接
G4Atlas
全转录组 RNA G-quadruplex (rG4) 综合数据库,整合了经实验验证和预测的高可信度 rG4 数据。
https://www.g4atlas.org/
QUADRatlas
整合人类 rG4 及其相互作用组资源。结合实验(rG4-seq、RT-stop 分析)和计算预测三种工具,确定了 217,424 个 rG4 区域。
https://rg4db.cibio.unitn.it/
EndoQuad
专注于内源性 G4(eG4)的专业数据库。提供经实验验证的全基因组 eG4 数据。
https://chenzxlab.hzau.edu.cn/EndoQuad/#/
G4Bank
数据库包含了13 个物种的 6,915,983 个 DNA G4 序列。
http://tubic.tju.edu.cn/g4bank/
参考文献
[1] Kwok CK et al. rG4-seq reveals widespread formation of G-quadruplex structures in the human transcriptome. Nat. Methods 13, 841–844 (2016).
[2] Yang SY et al. Transcriptome-wide identification of transient RNA G-quadruplexes in human cells. Nat. Chem. Biol. 14, 180–183 (2018).
[3] Yeung PY et al. Systematic evaluation and optimization of the experimental steps in RNA G-quadruplex structure sequencing. Sci. Rep. 9, 8091 (2019).
[4] Weng X et al. Keth-seq for transcriptome-wide RNA structure mapping. Nat. Chem. Biol. 16, 489–492 (2020).
[5] Hansel-Hertsch R et al. G-quadruplex structures mark human regulatory chromatin. Nat. Genet. 48, 1267–1272 (2016).
[6] Herviou P et al. hnRNP H/F drive RNA G-quadruplex-mediated translation linked to genomic instability and therapy resistance in glioblastoma. Nat. Commun. 11, 2661 (2020).
[7] Simko EAJ et al. G-quadruplexes offer a conserved structural motif for NONO recruitment to NEAT1 architectural lncRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, 7421–7438 (2020).
[8] Bolduc F et al. The small nuclear ribonucleoprotein polypeptide A (SNRPA) binds to the G-quadruplex of the BAG-1 5'UTR. Biochimie 176, 122–127 (2020).
[9] Guo JU et al. RNA G-quadruplexes are globally unfolded in eukaryotic cells and depleted in bacteria. Science. Sep 23;353(6306):aaf5371 (2016).
[10] von Hacht A et al. Identification and characterization of RNA guanine-quadruplex binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. Jun;42(10):6630-44 (2014).
[11] Haeusler et al. C9orf72 nucleotide repeat structures initiate molecular cascades of disease. Nature 507, 195–200 (2014).
[12] McRae EKS et al. Human DDX21 binds and unwinds RNA guanine quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Res. Jun 20;45(11):6656-6668 (2017).
[13] Serikawa T et al. Comprehensive identification of proteins binding to RNA G-quadruplex motifs in the 5' UTR of tumor-associated mRNAs. Biochimie. Jan;144:169-184 (2018).
[14] Herdy B et al. Analysis of NRAS RNA G-quadruplex binding proteins reveals DDX3X as a novel interactor of cellular G-quadruplex containing transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res. Nov 30;46(21):11592-11604 (2018).
[15] Yu H et al. G4Atlas: a comprehensive transcriptome-wide G-quadruplex database. Nucleic Acids Res. Jan 6;51(D1):D126-D134 (2023).
[16] Bourdon S et al. QUADRatlas: the RNA G-quadruplex and RG4-binding proteins database. Nucleic Acids Res. Jan 6;51(D1):D240-D247 (2023).
[17] Qian SH et al. EndoQuad: a comprehensive genome-wide experimentally validated endogenous G-quadruplex database. Nucleic Acids Res. Jan 5;52(D1):D72-D80 (2024).
[18] Zhong HS et al. G4Bank: A database of experimentally identified DNA G-quadruplex sequences. Interdiscip Sci. Sep;15(3):515-523 (2023).
[19] Birney E et al: An overview of Ensembl. Genome Res. May;14(5):925-8 (2004).

