

|
单细胞测序技术服务 靶向单细胞测序(lncRNA&mRNA) 单细胞测序 |
|
生物分子凝聚体研究 HyPro靶RNA临近标记技术 |
|
NGS测序技术服务 R-loop 测序(DRIPc-seq) |
|
NGS测序技术服务 环状DNA测序(eccDNA测序) |
|
Ribo-seq Ribo seq(ribosome profiling) |
核糖体-新生肽链复合物(RNC) RNC联合 circRNA芯片 RNC联合 lncRNA芯片 RNC-seq |
|
蛋白表达定量 DIA定量蛋白质组学 Label free非标定量 TMT标记定量 PRM靶向定量 |
康成生物|数谱生物表观转录组学测序通过RNA免疫沉淀测序(RNA-IP-Seq)分析定量检测表观转录组m6A, m1A, m5C, ac4C, m7G和Ψ修饰的情况。
技术优势:
●精湛的专业知识:在DNA/RNA修饰分析方面拥有数十年开发经验和技能。
●无限的检测范围:涵盖转录本任何区域中的m6A, m1A, m5C, ac4C, m7G和Ψ修饰位点。
●高分辨率:在修饰位点的 100 个碱基内精确定位峰值。
●高精确度:通过Input对照中的转录本丰度进行表观修饰水平的校准。
●严格的质量控制:通过qPCR 验证IP的优越富集效率。
●高分文章准备就绪:丰富的生信分析内容,包括修饰差异统计分析、修饰peak峰分布、motif识别等。
N4-乙酰胞嘧啶(N4-acetylcytidine, ac4C)是一种经典的rRNA和 tRNA 修饰,最近在mRNA 中也有发现[1]。NAT10是目前已知细胞中能够添加ac4C修饰的一种乙酰转移酶[1],ac4C峰的分布特点是:3'-UTR内的富集峰总体较少,而CDS和5'-UTR内的富集峰较多,且集中在翻译起始位点附近[1]。ac4C可稳定mRNA并促进翻译[1],特别是位于密码子摆动位点的 ac4C 可提高翻译效率[1]。mRNA乙酰化的生物功能和与疾病的关联在很大程度上仍然未知。有研究认为,依赖于NAT10的ac4C沉积在HIV-1 RNA上会增强病毒RNA的稳定性,从而促进HIV-1复制[2]。最近的一项研究表明,ac4C通过选择性招募PCBP2到IRES来增加 RNA 的稳定性,并促进RNA聚合酶与病毒RNA的结合,从而增强了肠道病毒 71(EV71)RNA 的复制和致病性[3]。
ac4C研究参考文献:
1. Arango D et al: Acetylation of Cytidine in mRNA Promotes Translation Efficiency. Cell 2018, 175(7):1872-1886 e1824.[PMID: 30449621]
2. Tsai K et al: Acetylation of Cytidine Residues Boosts HIV-1 Gene Expression by Increasing Viral RNA Stability. Cell Host Microbe 2020, 28(2):306-312 e306.[PMID: 32533923]
3. Hao H et al: N4-acetylcytidine regulates the replication and pathogenicity of enterovirus 71. Nucleic Acids Res 2022.[PMID: 35971620]
假尿嘧啶ψ是人类细胞中目前发现最丰富的RNA修饰,它存在于大多数类型的RNA中,例如mRNA[1, 2]上的假尿嘧啶化主要由PUS1 [3]、PUS7[4]和 TRUB1[4] 等酶完成,并且,有研究证明TRUB2和 RPUSD3参与线粒体mRNA中特定碱基的假尿嘧啶化[5]。mRNA编码区的ψ可通过促进含有ψ的密码子上氨基酸的替换来改变翻译产物[6]。RNA假尿嘧啶修饰以共转录的方式添加在前体mRNA(pre-mRNA)上,并可能影响pre-mRNA的可变剪接,使其富集于可变剪接区[7]。有趣的是,有研究在酵母中发现,同一个假尿嘧啶合成酶Pus6或许可以同时将ψ添加在mRNA和tRNA上,并由MetRS(蛋氨酸氨基酰tRNA合成酶)共同读取,这可能导致全局性和基因特异性翻译反应之间的协调[8]。另外还有一些研究表明,干扰素IFN可诱导干扰素刺激的基因转录本发生Ψ修饰,这表明Ψ在IFN信号通路和病毒防御中发挥作用 [9]。
Ψ研究参考文献:
1. Carlile TM et al: Pseudouridine profiling reveals regulated mRNA pseudouridylation in yeast and human cells. Nature 2014, 515(7525):143-146.[PMID: 25192136]
2. Schwartz S et al: Transcriptome-wide mapping reveals widespread dynamic-regulated pseudouridylation of ncRNA and mRNA. Cell 2014, 159(1):148-162.[PMID: 25219674]
3. Carlile TM et al: mRNA structure determines modification by pseudouridine synthase 1. Nat Chem Biol 2019, 15(10):966-974.[PMID: 31477916]
4. Safra M et al: TRUB1 is the predominant pseudouridine synthase acting on mammalian mRNA via a predictable and conserved code. Genome Res 2017, 27(3):393-406.[PMID: 28073919]
5. Antonicka H et al: A pseudouridine synthase module is essential for mitochondrial protein synthesis and cell viability. EMBO Rep 2017, 18(1):28-38.[PMID: 27974379]
6. Eyler DE et al: Pseudouridinylation of mRNA coding sequences alters translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116(46):23068-23074.[PMID: 31672910]
7. Martinez NM et al: Pseudouridine synthases modify human pre-mRNA co-transcriptionally and affect pre-mRNA processing. Mol Cell 2022, 82(3):645-659 e649.[PMID: 35051350]
8. Huang S et al: Interferon inducible pseudouridine modification in human mRNA by quantitative nanopore profiling. Genome Biol 2021, 22(1):330.[PMID: 34872593]
转录本的RNA修饰水平定量统计:
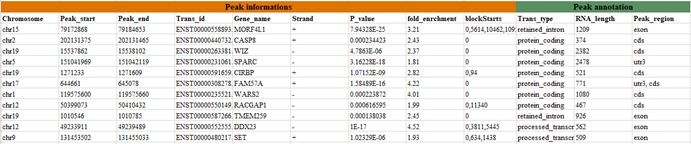
RNA表观修饰在转录组中的peak分布:
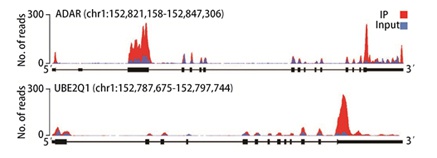
图1:human ADAR1和UBE2Q1 mRNA中的修饰peak通过基因组浏览器中提供的track文件进行可视化展示。
RNA修饰峰reads数目在mRNA各种区域的分布情况:
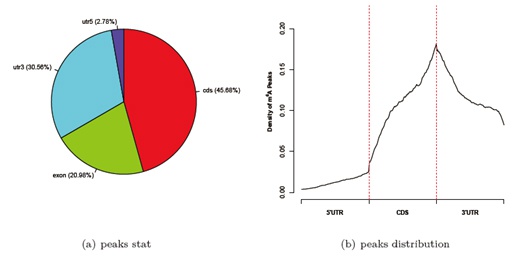
图2:mRNA 的 5'UTR、CDS 和 3'UTR 区域的RNA修饰峰统计(a)和密度分布(b)。
RNA 修饰peak序列的motif分析:


图3:用 DREME 算法识别出RNA表观修饰测序的motif,并以序列图表示。
样本需求 :
纯化的total RNA,冷冻组织或细胞沉淀;
有关如何启动项目的详细信息,请参阅样本采集指南。
1.总 RNA 分离纯化(可选);
2.从总 RNA 中进行 RNA QC 和 mRNA 分离;
3.mRNA 片段化处理;
4.用相应修饰的抗体进行IP;
5.通过 qPCR 进行 IP 效率质控;
6.测序文库制备;
7.簇生成;
8.利用Illumina平台测序;
9.数据分析,包括reads比对、peak鉴定、peak定量分析和注释、motif分析、差异m1A修饰峰值分析、GO和Pathway分析。

