

|
单细胞测序技术服务 靶向单细胞测序(lncRNA&mRNA) 单细胞测序 |
|
生物分子凝聚体研究 HyPro靶RNA临近标记技术 |
|
NGS测序技术服务 环状DNA测序(eccDNA测序) |
|
Ribo-seq Ribo seq(ribosome profiling) |
核糖体-新生肽链复合物(RNC) RNC联合 circRNA芯片 RNC联合 lncRNA芯片 RNC-seq |
|
蛋白表达定量 DIA定量蛋白质组学 Label free非标定量 TMT标记定量 PRM靶向定量 |
蛋白修饰定量 N-糖基化蛋白组学 乳酸化修饰蛋白质组学 O-GlcNAc修饰蛋白质组学 |
作为一种新型的tRNA来源的非编码小RNA,tRF& tiRNA由精确调控的生物发生过程所产生,参与行使多种生物学功能: 作为microRNA参与RNA干扰;调节靶向mRNA的稳定性;在细胞应激条件下促进应激颗粒(SG)的组装;调控细胞凋亡[1];作为表观遗传因子在世代间传递[2,3](图1)。tRFs&tiRNAs的组成和含量高度依赖于细胞类型,并且与多种病理状态密切相关。它们在生物体液中广泛存在,含量远超microRNA,使之有望成为优质的分子标志物[4-7]。
Arraystar nrStar™ Human tRF & tiRNA PCR 芯片检测185个数据库收录和新近文献报道的人tRF&tiRNA。Arraystar nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR芯片检测从tRFdb数据库中挑选的88个常见的小鼠tRFs。
产品列表
| 芯片名称 | 货号 | 规格 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|---|
| nrStarTM Human tRF&tiRNA PCR Array | AS-NR-002-1 | 384-well(2*192) / plate | 检测185个数据库收录和新近文献报道的人tRF&tiRNA |
| nrStarTM Human tRF&tiRNA PCR Array (Roche Light Cycler 480) | AS-NR-002-1-R | 384-well (2*192) / plate | |
| nrStarTM Mouse tRF PCR Array | AS-NR-002M-1 | 384-well (4*96) / plate | 检测从tRFdb数据库中挑选的88个新近常见的小鼠tRFs |
| nrStarTM Mouse tRF PCR Array (Roche Light Cycler 480) | AS-NR-002M-1-R | 384-well (4*96) / plate |
优势
• 前沿-关注近些年火热的tRF&tiRNA研究
• 聚焦-检测具有生物学潜能的tRF&tiRNA
• 精确检测-所有引物都经过精心设计、优化和验证
• 简单便捷-标准的qPCR板设计,直接使用,无需预扩增
为保证能区分tRF&tiRNA和其前体,同时为获得更好的检测特异性,需配套使用rtStar™ First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (3’and 5’adaptor) (cat # AS-FS-003 )
tRF& tiRNA参与行使多种生物学功能: 作为microRNA参与RNA干扰;调节靶向mRNA的稳定性;在细胞应激条件下促进应激颗粒(SG)的组装;调控细胞凋亡;作为表观遗传因子在世代间传递 [1] (图1)。tRFs&tiRNAs的组成和含量高度依赖于细胞类型,并且与多种病理状态密切相关。它们在生物体液中广泛存在,含量远超microRNA,使之有望成为优质的分子标志物[2-5]。
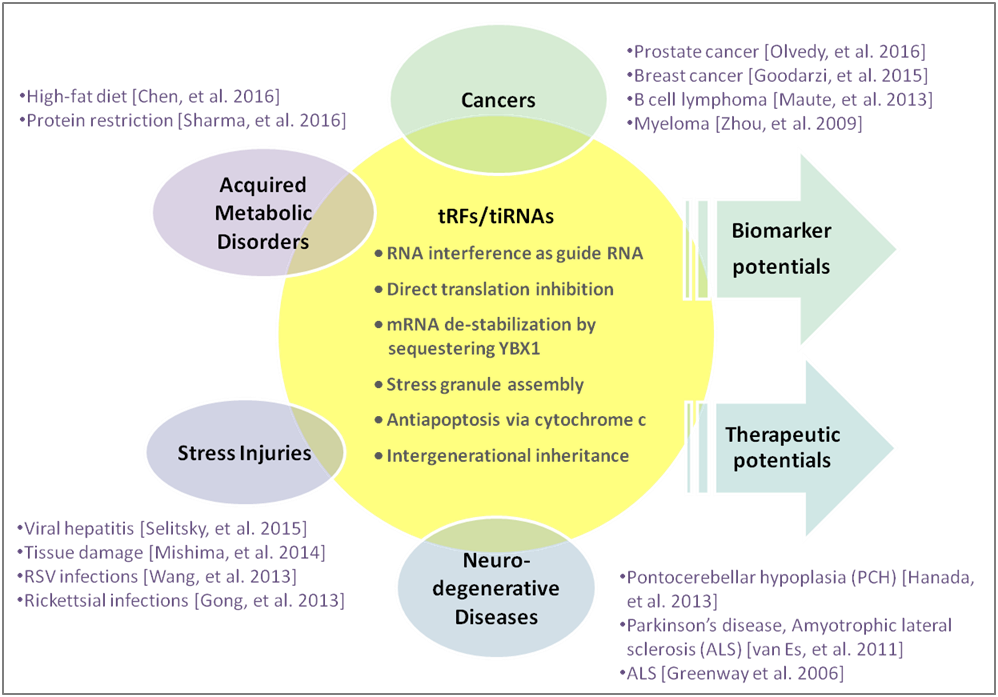
图1. tRFs&tiRNAs分子功能和人类疾病。
tRFs&tiRNAs 是由tRNA或pre-tRNA经过精确剪切形成的。因序列上的重合,常规qPCR的方法很难将tRF&tiRNA和tRNA或pre-tRNA区分开来。同时,由于tRFs&tiRNAs序列长度只有16-50nt,序列太短,很难直接使用qPCR进行检测。Arraystar借鉴了经典的小RNA测序建库方法,通过在tRFs&tiRNAs 的3’和5’端分别加上一段序列来延长序列长度。正向和反向引物分别与5'和3'连接处的序列互补配对,以此有效地区分tRF&tiRNA与其前体及其他小RNA,从而能可靠、准确地检测tRF&tiRNA的表达(图2)。

图2. 通过在5’和 3’端加上接头, nrStar™ tRF&tiRNA PCR 芯片可以精确检测指定的tRFs&tiRNAs而不扩增其前体tRNAs或pre-tRNAs.
Arraystar nrStar™ tRF&tiRNA PCR 芯片体系,能快速便捷地特异性检测tRFs & tiRNAs,共包含两款产品:用于接头连接和cDNA 合成的Arraystar rtStar™ First-Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (3’and 5’adaptor) 及用于tRF&tiRNA检测的 Arraystar nrStar™ tRF&tiRNA PCR 芯片。
Reference
1. Anderson P. and P. Ivanov (2014) "tRNA fragments in human health and disease." FEBS Lett. 588(23):4297-304 [PMID: 25220675]
2. Telonis, A. G. et al. Dissecting tRNA-derived fragment complexities using personalized transcriptomes reveals novel fragment classes and unexpected dependencies. Oncotarget 6, 24797-24822, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.4695 (2015). [PMID: 26325506].
3. Olvedy, M. et al. A comprehensive repertoire of tRNA-derived fragments in prostate cancer. Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8293 (2016). [PMID: 27015120].
4. Schageman, J. et al. The complete exosome workflow solution: from isolation to characterization of RNA cargo. BioMed research international 2013, 253957, doi:10.1155/2013/253957 (2013). [PMID: 24205503].
5. Dhahbi, J. M. et al. 5' tRNA halves are present as abundant complexes in serum, concentrated in blood cells, and modulated by aging and calorie restriction. BMC genomics 14, 298, doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-298 (2013). [PMID: 23638709].
6. Kumar, P., Mudunuri, S. B., Anaya, J. & Dutta, A. tRFdb: a database for transfer RNA fragments. Nucleic acids research 43, D141-145, doi:10.1093/nar/gku1138 (2015). [PMID: 25392422].
|
Human tRFs&tiRNAs (185) |
|
tRF-1 1001, 1003, 1004, 1005, 1006, 1007, 1010, 1012, 1013, 1015, 1020, 1025, 1026, 1027, 1028, 1029, 1030, 1031, 1032, 1033, 1035, 1036, 1037, 1038, 1039, 1040, 1041, 1042 tRF-3 3002B, 3004B, 3006B, 3031B, 3033A, 3030A, 3030B, 3002A, 3003A, 3003B, 3006A, 3008A, 3008B, 3009B, 3011/12A, 3016/18/22B, 3017A, 3017B, 3019/20/21B, 3026B, 3027/28B, 3019A, 3020/21A, 3022A, 3026/27/28A, 3029A, 3031A tRF-5 5001A, 5001B, 5002A, 5002B, 5008B, 5009A, 5009B, 5010A, 5011A, 5012B, 5013B, 5015/17A, 5016A, 5019A, 5019B, 5020/21A, 5020B, 5021B, 5022A, 5022B, 5023B, 5024A, 5026A, 5026/27B, 5028/29A, 5028/29B, 5032A, 5032B, TRF21-26, TRF63, TRF23, TRF205, TRF208, TRF223, TRF250, TRF272/274, TRF273, TRF293/294, TRF305/306/307, TRF308, TRF312, TRF316, TRF318, TRF320, TRF321, TRF322, TRF323/324/326, TRF337-339, TRF347, TRF351, TRF354, TRF356/359, TRF368, TRF366, TRF365, TRF373, TRF374, TRF375, TRF393, TRF396, TRF417, TRF457, TRF460, TRF462, TRF463, TRF466/468/469/471/472/473, TRF490, TRF492, TRF493, TRF511, TRF524, TRF533/534, TRF537, TRF546/547, TRF550/551
tiRNA-3 (3’ tRNA half) 3'tiR_007_GluTTC (n), 3'tiR_012_ArgCCT (n), 3'tiR_026_GlnCTG (n), 3'tiR_028_HisGTG (mt), 3'tiR_037_ArgCCG (n), 3'tiR_056_ValTAC (mt), 3'tiR_060_MetCAT (n), 3'tiR_063_ArgCCT (n), 3'tiR_075_GluTTC (mt)/ GluTTC (mt-la), 3'tiR_078_ArgTCT (n), 3'tiR_080_ProTGG (mt), 3'tiR_082_ThrTGT (mt), 3'tiR_088_LysCTT (n) tiRNA-5 (5’ tRNA half) 5003/4C, 5008C, 5009C, 5016C, 5026/27C, TRF62, TRF315, TRF327, TRF353, TRF419, tiRNA-5033-ProTGG-1, tiRNA-5033-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5029-GlyGCC-2, tiRNA-5034-ValCAC-2, tiRNA-5034-ValCAC-3, tiRNA-5030-HisGTG-1, tiRNA-5030-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5033-GluTTC-2, tiRNA-5030-LysCTT-2, tiRNA-5029-ProAGG, tiRNA-5031-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5031-HisGTG-1, tiRNA-5031-GluCTC-1, tiRNA-5034-GlyCCC-1, tiRNA-5034-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5033-LysTTT-1, tiRNA-5032-LysTTT-1, tiRNA-5031-PheGAA, tiRNA-5034-ValTAC-3, tiRNA-5030-GlnTTG-3, tiRNA-5029-GlyGCC-3, tiRNA-5035-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5035-GluTTC-2, tiRNA-5034-GluTTC-2, tiRNA-5035-GluTTC-3, tiRNA-5032-GluTTC-1, tiRNA-5035-GluCTC, tiRNA-5030-SerGCT-3, tiRNA-5030-SerGCT-1, tiRNA-5031-HisGTG-2, tiRNA-5029-AlaAGC-1, tiRNA-5032-LysCTT-1 |
|
Mouse tRF (88) |
|
tRF-1 1003, 1006, 1008, 1009, 1010, 1015, 1016, 1019, 1020, 1026, 1035 tRF-3 3001b, 3002a/3035a, 3003a, 3004b, 3005a, 3006a, 3009a, 3009b, 3010a, 3010b/3017b, 3011a, 3011b, 3012b, 3017a, 3017b/3010b, 3019a, 3019b/3020b, 3021a, 3023b, 3024b/3046b, 3025a, 3025b, 3026a, 3027a, 3028b/3029b, 3029a, 3030a, 3031a, 3031b, 3032a, 3032b, 3033a, 3033b, 3034a, 3036a, 3036b/3037b, 3038a, 3038b, 3039a, 3041b/3042b, 3043a, 3043b, 3044a, 3044b, 3045a, 3046a, 3047b, 3048a, 3050a, 3051a, 3052a tRF-5 5001a/5001b/5010a, 5002b/5004b, 5005a/5006b, 5005b, 5006a, 5006c, 5007a, 5009a, 5009b, 5011a, 5011b/5012b, 5012b, 5013a, 5013b, 5013b/5017b/5018b, 5014a, 5014a/5015a, 5014b, 5016a, 5019a, 5019b, 5020b/5021a, 5022a, 5022b, 5023b/24b |
Database
tRFdb http://genome.bioch.virginia.edu/trfdb/
MINTbase https://cm.jefferson.edu/MINTbase/
Reference
Olvedy, M. et al. A comprehensive repertoire of tRNA-derived fragments in prostate cancer. Oncotarget, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.8293 (2016).
Selitsky SR, Baran-Gale J, Honda M, Yamane D, Masaki T, Fannin EE, et al. Small tRNA-derived RNAs are increased and more abundant than microRNAs in chronic hepatitis B and C. Scientific reports 2015;5:7675.
Wang Q, Lee I, Ren J, Ajay SS, Lee YS, Bao X. Identification and functional characterization of tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs) in respiratory syncytial virus infection. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2013;21:368-79.
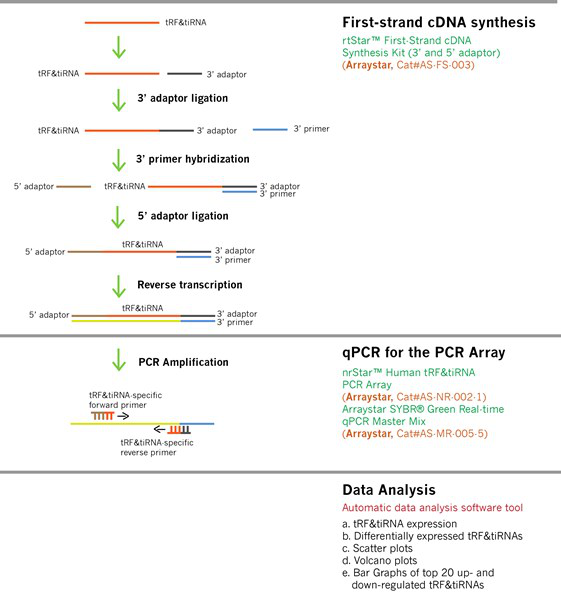
图1. tRF&tiRNA qPCR芯片实验流程
适用的qPCR仪:
• ABI ViiA™ 7
• ABI 7500 & ABI 7500 FAST
• ABI 7900HT
• ABI QuantStudio™ 6 Flex Real-Time PCR system
• ABI QuantStudio™ 7 Flex Real-Time PCR system
• ABI QuantStudio™ 12K Flex Real-Time PCR System
• Bio-Rad CFX384
• Bio-Rad iCycler & iQ Real-Time PCR Systems
• Eppendorf Realplex
• QIAGEN Rotor Gene Q 100
• Roche Light Cycler 480
Aksomics使用Arraystar的芯片为客户提供服务,该产品说明书及分析工具见下:
产品说明书:
 Manual_nrStar_Human_tRF_tiRNA_PCR_Array_v1.04
Manual_nrStar_Human_tRF_tiRNA_PCR_Array_v1.04
 Manual_nrStar™_Mouse_tRF_PCR_Array_v1.01
Manual_nrStar™_Mouse_tRF_PCR_Array_v1.01
工具:
 Analysis_Tool_for_nrStar™_Human_tRF_tiRNA_PCR_Array_v1.01
Analysis_Tool_for_nrStar™_Human_tRF_tiRNA_PCR_Array_v1.01
 Analysis tool for nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR Array_v1.0
Analysis tool for nrStar™ Mouse tRF PCR Array_v1.0

